最近还是很喜欢用golang来刷算法题,更接近通用算法,也没有像动态脚本语言那些语法糖,真正靠实力去解决问题。
下面这道题很有趣,也是一道链表题目,具体如下:
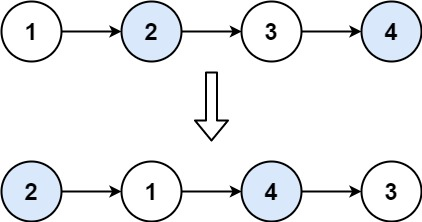
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs
Solved
Medium
Topics
Companies
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and r服务器托管eturn its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [2,1,4,3]
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 100].
0 快速思考了一下,想到这个交换节点的事儿可以用递归去实现,通过三个指针prev, current, next不断移动,实现相邻节点交换,代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
if head.Next.Next == nil {
next := head.Next
head.Next = nil
next.Next = head
head = next
return head
}
prev, cur, nxt := head, head.Next, head.Next.Next
cur.Next = prev
head = cur
prev.Next = swapPairs(nxt)
return head
}
递归虽然好,但是也会有一些性能上的担忧,毕竟递归调用太深,可能会引发堆栈溢出。后面再仔细推敲了一下,完全可以用2个指针不断进行交换,可以不用递归。这里还是要用一个dump节点来方便的保存修改后的链表,具体如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dump := &ListNode{Val: 0}
dump.Next = head
prevNode := dump
currentNode := head
for currentNode != nil && currentNode.Next != nil {
prevNode.Next = currentNode.Next
currentNode.Next = currentNode.Next.Next
prevNode.Next.Next = currentNode
prevNode = currentNode
currentNode = currentNode.Next
}
return dump.Next
}
最终它们的时间复杂度是O(N),空间复杂度O(1),都非常棒。如果是你,你更喜欢哪种解法呢?欢迎在评论区留言交流。
服务器托管,北京服务器服务器托管托管,服务器租用 http://www.fwqtg.net
机房租用,北京机房租用,IDC机房托管, http://www.fwqtg.net
【开源中国 APP 全新上线】“动弹” 回归、集成大模型对话、畅读技术报告” 为了帮助开发人员更迅速地识别错误类型、定位和处理问题,我们整理了DolphinDB Server中的异常以及关键错误信息,总结出了一份DolphinDB 数据库错误代码列表。当发生报…

