前面基础管理的功能基本开发完了,接下来我们来优化一下开发功能,来添加EventBus功能。
EventBus也是我们使用场景非常广的东西。这里我会实现一个本地的EventBus以及分布式的EventBus。
分别使用MediatR和Cap来实现。
现在简单介绍一下这两者:
MediatR是一个轻量级的中介者库,用于实现应用程序内部的消息传递和处理。它提供了一种简单而强大的方式来解耦应用程序的不同部分,并促进了代码的可维护性和可测试性。使用MediatR,您可以定义请求和处理程序,然后通过发送请求来触发相应的处理程序。这种模式使得应用程序的不同组件可以通过消息进行通信,而不需要直接引用彼此的代码。MediatR还提供了管道处理功能,可以在请求到达处理程序之前或之后执行一些逻辑,例如验证、日志记录或缓存。
Cap是一个基于.NET的分布式事务消息队列框架,用于处理高并发、高可靠性的消息传递。它支持多种消息队列中间件,如RabbitMQ、Kafka和Redis。Cap提供了一种可靠的方式来处理分布式事务,确保消息的可靠传递和处理。它还支持事件发布/订阅模式,使得不同的服务可以通过发布和订阅事件来进行解耦和通信。Cap还提供了一些高级功能,如消息重试、消息顺序处理和消息回溯,以应对各种复杂的场景。
总结来说,MediatR适用于应用程序内部的消息传递和处理,它强调解耦和可测试性。而Cap则更适合处理分布式系统中的消息传递和事务,它提供了高可靠性和高并发的支持,并且适用于处理复杂的分布式场景。
定义接口
添加一个ILocalEventBus接口,里面包含一个PublishAsync事件发布方法。
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Local
{
public interface ILocalEventBus
{
Task PublishAsync(TEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
}
添加一个IDistributedEventBus接口,里面包含一个PublishAsync事件发布方法。
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Distributed
{
public interface IDistributedEventBus
{
Task PublishAsync(TEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
}
添加一个IEventHandler的空接口,作为事件处理的基础接口
namespace Wheel.EventBus
{
public interface IEventHandler
{
}
}
LocalEventBus
这里我们用MediatR的Notification来实现我们的本地事件总线。
首先安装MediatR的Nuget包。
MediatREventBus
然后实现MediatREventBus,这里其实就是包装以下IMediator.Publish方法。
using MediatR;
using Wheel.DependencyInjection;
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Local.MediatR
{
public class MediatREventBus : ILocalEventBus, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly IMediator _mediator;
public MediatREventBus(IMediator mediator)
{
_mediator = mediator;
}
public Task PublishAsync(TEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
return _mediator.Publish(eventData, cancellationToken);
}
}
}
添加一个ILocalEventHandler接口,用于处理LocalEventBus发出的内容。这里由于MediatR的强关联,必须继承INotification接口。
using MediatR;
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Local
{
public interface ILocalEventHandler : IEventHandler, INotificationHandler where TEventData : INotification
{
Task Handle(TEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
}
然后我们来实现一个MediatR的INotificationPublisher接口,由于默认的两种实现方式都是会同步阻塞请求,所以我们单独实现一个不会阻塞请求的。
using MediatR;
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Local.MediatR
{
public class WheelPublisher : INotificationPublisher
{
public Task Publish(IEnumerable handlerExecutors, INotification notification, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
return Task.Factory.StartNew(async () =>
{
foreach (var handler in handlerExecutors)
{
await handler.HandlerCallback(notification, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}, cancellationToken);
}
}
}
接下来添加一个扩展方法,用于注册MediatR。
namespace Wheel.EventBus
{
public static class EventBusExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddLocalEventBus(this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMediatR(cfg =>
{
cfg.RegisterServicesFromAssemblies(Directory.GetFiles(AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory, "*.dll")
.Where(x => !x.Contains("Microsoft.") && !x.Contains("System."))
.Select(x => Assembly.Load(AssemblyName.GetAssemblyName(x))).ToArray());
cfg.NotificationPublisher = new WheelPublisher();
cfg.NotificationPublisherType = typeof(WheelPublisher);
});
return services;
}
}
}
这里通过程序集注册,会自动注册所有集成MediatR接口的Handler。
然后指定NotificationPublisher和NotificationPublisherType是我们自定义的Publisher。
就这样我们完成了LocalEventBus的实现,我们只需要定义我们的EventData,同时实现一个ILocalEventHandler,即可完成一个本地事件总线的处理。
DistributedEventBus
这里我们通过CAP来实现我们的分布式事件总线。
首先需要安装DotNetCore.CAP的相关NUGET包。如消息队列使用RabbitMQ则安装DotNetCore.CAP.RabbitMQ,使用Redis则DotNetCore.CAP.RedisStreams,数据库存储用Sqlite则使用DotNetCore.CAP.Sqlite。
CapDistributedEventBus
这里CapDistributedEventBus的实现其实就是包装以下Cap的ICapPublisher.PublishAsync方法。
using DotNetCore.CAP;
using System.Reflection;
using Wheel.DependencyInjection;
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Distributed.Cap
{
public class CapDistributedEventBus : IDistributedEventBus, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly ICapPublisher _capBus;
public CapDistributedEventBus(ICapPublisher capBus)
{
_capBus = capBus;
}
public Task PublishAsync(TEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
var sub = typeof(TEventData).GetCustomAttribute()?.Name;
return _capBus.PublishAsync(sub ?? nameof(eventData), eventData, cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
}
}
}
这里使用了一个EventNameAttribute,这个用于自定义发布的事件名称。
using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis;
namespace Wheel.EventBus
{
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)]
public class EventNameAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public EventNameAttribute([NotNull] string name)
{
Name = name;
}
public static string? GetNameOrDefault()
{
return GetNameOrDefault(typeof(TEvent));
}
public static string? GetNameOrDefault([NotNull] Type eventType)
{
return eventType
.GetCustomAttributes(true)
.OfType()
.FirstOrDefault()
?.GetName(eventType)
?? eventType.FullName;
}
public string? GetName(Type eventType)
{
return Name;
}
}
}
添加一个IDistributedEventHandler接口,用于处理DistributedEventBus发出的内容。
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Distributed
{
public interface IDistributedEventBus
{
Task PublishAsync(TEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default);
}
}
这里由于对CAP做了2次封装,所以需要重写一下ConsumerServiceSelector。
using DotNetCore.CAP;
using DotNetCore.CAP.Internal;
using System.Reflection;
using TopicAttribute = DotNetCore.CAP.Internal.TopicAttribute;
namespace Wheel.EventBus.Distributed.Cap
{
public class WheelConsumerServiceSelector : ConsumerServiceSelector
{
protected IServiceProvider ServiceProvider { get; }
///
/// Creates a new .
///
public WheelConsumerServiceSelector(IServiceProvider serviceProvider) : base(serviceProvider)
{
ServiceProvider = serviceProvider;
}
protected override IEnumerable FindConsumersFromInterfaceTypes(IServiceProvider provider)
{
var executorDescriptorList = base.FindConsumersFromInterfaceTypes(provider).ToList();
using var scope = provider.CreateScope();
var scopeProvider = scope.ServiceProvider;
//handlers
var handlers = scopeProvider.GetServices()
.Select(o => o.GetType()).ToList();
foreach (var handler in ha服务器托管网ndlers)
{
var interfaces = handler.GetInterfaces();
foreach (var @interface in interfaces)
{
if (!typeof(IEventHandler).GetTypeInfo().IsAssignableFrom(@interface))
{
continue;
}
var genericArgs = @interface.GetGenericArguments();
if (genericArgs.Length != 1)
{
continue;
}
if (!(@interface.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(IDistributedEventHandler)))
{
continue;
}
var descriptors = GetHandlerDescription(genericArgs[0], handler);
foreach (var descriptor in descriptors)
{
var count = executorDescriptorList.Count(x =>
x.Attribute.Name == descriptor.Attribute.Name);
descriptor.Attribute.Group = descriptor.Attribute.Group.Insert(
descriptor.Attribute.Group.LastIndexOf(".", StringComparison.Ordinal), $".{count}");
executorDescriptorList.Add(descriptor);
}
}
}
return executorDescriptorList;
}
protected virtual IEnumerable GetHandlerDescription(Type eventType, Type typeInfo)
{
var serviceTypeInfo = typeof(IDistributedEventHandler)
.MakeGenericType(eventType);
var method = typeInfo
.GetMethod(
nameof(IDistributedEventHandlerWheelConsumerServiceSelector的主要作用是动态的给我们的IDistributedEventHandler打上CapSubscribeAttribute特性,使其可以正确订阅处理CAP的消息队列。
接下来添加一个扩展方法,用于注册CAP。
using DotNetCore.CAP.Internal;
using System.Reflection;
using Wheel.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Wheel.EventBus.Distributed.Cap;
using Wheel.EventBus.Local.MediatR;
namespace Wheel.EventBus
{
public static class EventBusExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddDistributedEventBus(this IServiceCollection services, IConfiguration configuration)
{
services.AddSingleton();
services.AddCap(x =>
{
x.UseEntityFramework();
x.UseSqlite(configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"));
//x.UseRabbitMQ(configuration["RabbitMQ:ConnectionString"]);
x.UseRedis(configuration["Cache:Redis"]);
});
return services;
}
}
}
就这样我们完成了DistributedEventBus的实现,我们只需要定义我们的EventData,同时实现一个IDistributedEventHandler,即可完成一个分布式事件总线的处理。
启用EventBus
在Program中添加两行代码,这样即可完成我们本地事件总线和分布式事件总线的集成了。
builder.Services.AddLocalEventBus();
builder.Services.AddDistributedEventBus(builder.Configuration);
测试效果
添加一个TestEventData,这里为了省事,我就公用一个EventData类
using MediatR;
using Wheel.EventBus;
namespace Wheel.TestEventBus
{
[EventName("Test")]
public class TestEventData : INotification
{
public string TestStr { get; set; }
}
}
一个TestEventDataLocalEventHandler,这里注意的是,实现ILocalEventHandler不需要额外继承ITransientDependency,因为MediatR会自动注册所有继承INotification接口的实现。否则会出现重复执行两次的情况。
using Wheel.DependencyInjection;
using Wheel.EventBus.Local;
namespace Wheel.TestEventBus
{
public class TestEventDataLocalEventHandler : ILocalEventHandler
{
private readonly ILogger _logger;
public TestEventDataLocalEventHandler(ILogger logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public Task Handle(TestEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"TestEventDataLocalEventHandler: {eventData.TestStr}");
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
}
一个TestEventDataDistributedEventHandler
using Wheel.DependencyInjection;
using Wheel.EventBus.Distributed;
namespace Wheel.TestEventBus
{
public class TestEventDataDistributedEventHandler : IDistributedEventHandler, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly ILogger _logger;
public TestEventDataDistributedEventHandler(ILogger logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public Task Handle(TestEventData eventData, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
_logger.LogWarning($"TestEventDataDistributedEventHandler: {eventData.TestStr}");
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
}
EventHandler通过日志打印数据。
添加一个API控制器用于测试调用
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Wheel.TestEventBus;
namespace Wheel.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
[AllowAnonymous]
public class TestEventBusController : WheelControllerBase
{
[HttpGet("Local")]
public async Task Local()
{
await LocalEventBus.PublishAsync(new TestEventData { TestStr = GuidGenerator.Create().ToString() });
return Ok();
}
[HttpGet("Distributed")]
public async Task Distributed()
{
await DistributedEventBus.PublishAsync(new TestEventData { TestStr = GuidGenerator.Create().ToString() });
return Ok();
}
}
}
启用程序,调用API,可以看到,都成功执行了。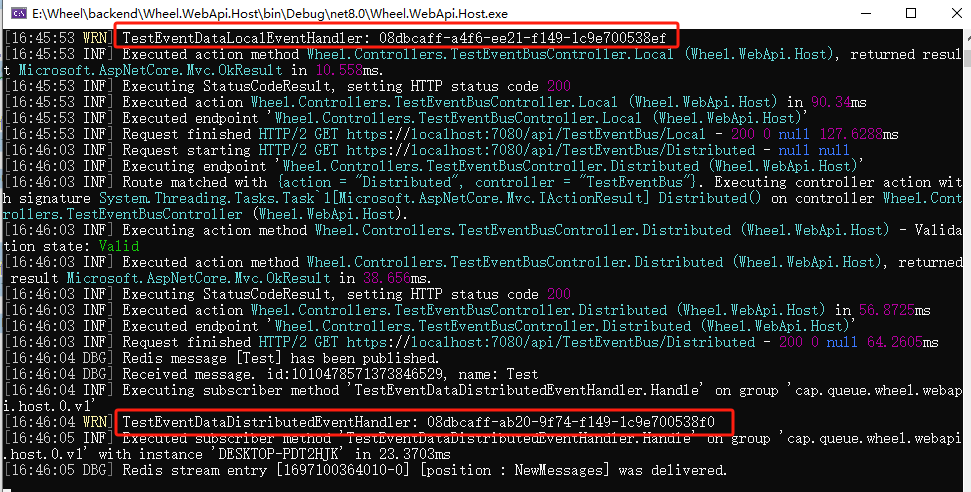
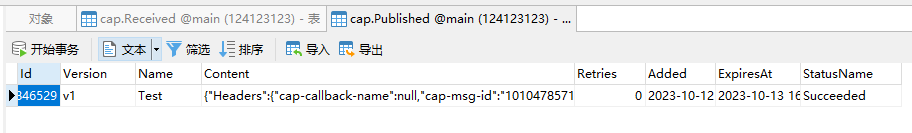
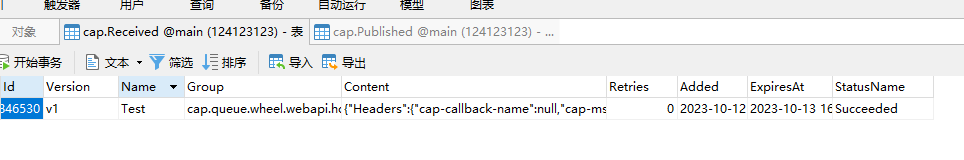
CAP的本地消息表也可以看到正常的发送接收。
到这我们就完成了我们EventBus的集成了。
轮子仓库地址https://github.com/Wheel-Framework/Wheel
欢迎进群催更。

服务器托管,北京服务器托管,服务器租用 http://www.fwqtg.net
机房租用,北京机房租用,IDC机房托管, http://www.fwqtg.net
相关推荐: 第四章 网络层【计算机网络】
前言
推荐
第四章 网络层
最后第四章 网络层【计算机网络】 前言 推荐 第四章 网络层 4.1 网络层的几个重要概念 4.1.1 网络层提供的两种服务 4.1.2 网络层的两个层面 例-路由表的建立 4.2网际协议IP 4.2.1 虚拟互连网络 4.2.2 IP地址 例-分类地址练习 例-…

