本文主要通过例子介绍了如何给核函数计时的思路和实现。实现例子代码参考文献[7],只需要把相应章节对应的CMakeLists.txt文件拷贝到CMake项目根目录下面即可运行。
1.用CPU计时器计时(sumArraysOnGPU-timer.cu)[7]
在主函数中用CPU计时器测试向量加法的核函数,如下所示:
#include // 包含cuda运行时系统的头文件
#include // 包含标准输入输出函数的头文件
#include // 包含时间函数的头文件
#include // 包含时间函数的头文件
//#define CHECK(call) // 定义CHECK宏函数
void initialData(float *ip, int size)
{
// 为随机数生成不同的种子
time_t t; // time_t是一种时间类型
srand((unsigned int) time(&t)); // time()函数返回当前时间的秒数
for (int i = 0; i epsilon) // 如果误差超过范围
{
match = 0; // 匹配标志置0
printf("Arrays do not match!n"); // 打印提示信息
printf("host %5.2f gpu %5.2f at current %dn", hostRef[i], gpuRef[i], i); // 打印不匹配的元素
break;
}
}
if (match) printf("Arrays match.nn"); // 如果匹配,打印提示信息
}
void sumArraysOnHost(float *A, float *B, float *C, const int N) // 在主机上计算
{
for (int idx = 0; idx tv_sec = static_cast(timebuffer.time); // 转换为秒
tp->tv_usec = timebuffer.millitm * 1000; // 转换为微秒
return 0; // 返回0
}
double cpuSecond() { // 定义cpuSecond函数
struct timeval tp; // 定义timeval结构体
gettimeofday(&tp, NULL); // 获取当前时间
return ((double) tp.tv_sec + (double) tp.tv_usec * 1.e-6); // 返回当前时间
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
printf("%s Starting...n", argv[0]); // 打印提示信息
// 设置device
int dev = 0; // 定义device
cudaDeviceProp deviceProp; // 定义deviceProp结构体
// CHECK(cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProp, dev)); // 获取deviceProp结构体
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&deviceProp, dev); // 获取deviceProp结构体
printf("Using Device %d: %sn", dev, deviceProp.name);
// CHECK(cudaSetDevice(dev)); // 设置device
cudaSetDevice(dev); // 设置device
// 设置vector数据大小
int nElem = 1 >>(d_A, d_B, d_C); // 调用kernel
cudaDeviceSynchronize(); // 同步device
iElaps = cpuSecond() - iStart; // 记录结束时间
printf("sumArraysOnGPU >> Time elapsed %f secn", grid.x, block.x, iElaps); // 打印执行时间
服务器托管网 // 拷贝结果到主机
cudaMemcpy(gpuRef, d_C, nBytes, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// 检查结果
checkResult(hostRef, gpuRef, nElem);
// 释放设备内存
cudaFree(d_A);
cudaFree(d_B);
cudaFree(d_C);
// 释放主机内存
free(h_A);
free(h_B);
free(hostRef);
free(gpuRef);
return 0;
}
输出结果,如下所示:
Using Device 0: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090
Vector size 16777216
sumArraysOnHost Time elapsed 0.059000 sec
sumArraysOnGPU >> Time elapsed 0.001000 sec
Arrays match.
2.用nvprof工具计时(已过时)
nvprof命令行工具可以从应用程序的CPU和GPU活动中获取时间线信息,包括内核执行、内存传输以及CUDA API的调用。使用语法如下所示:
$ nvprof [nvprof_args] [application_args]
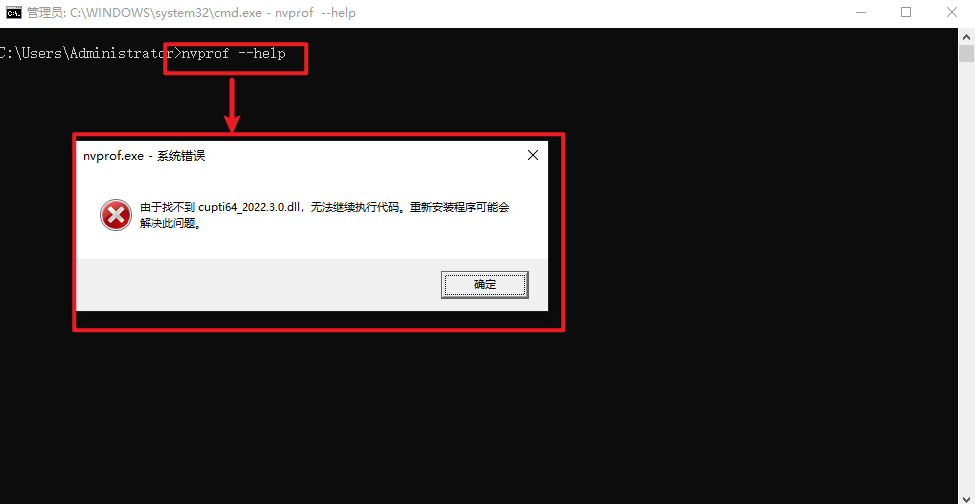
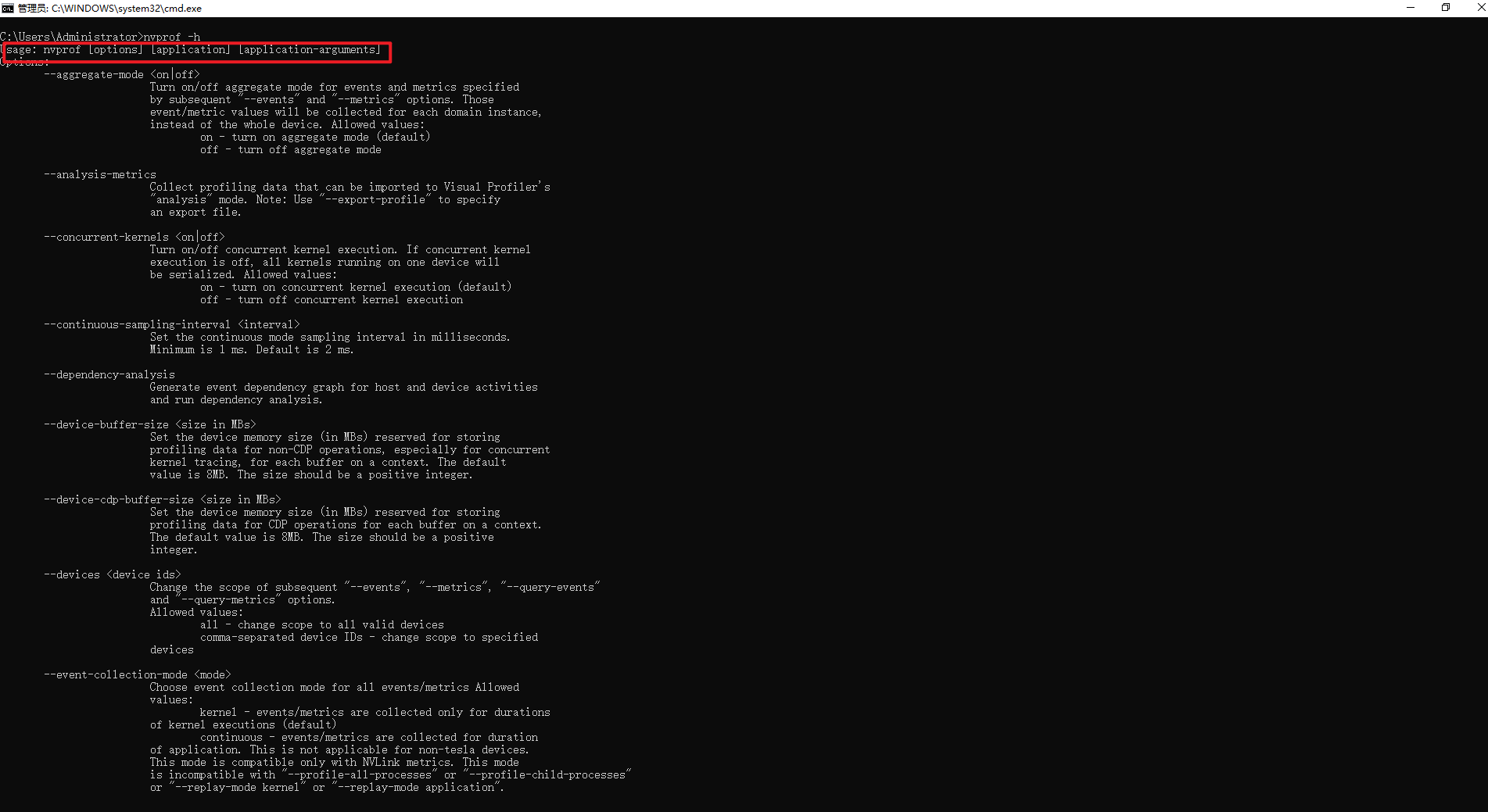
$ nvprof --help
$ nvprof ./sumArraysOnGPU-timer
遇到这个错误,将C:Program FilesNVIDIA GPU Computing ToolkitCUDAv11.8extrasCUPTIlib64添加到Path环境变量中即可,如下所示:
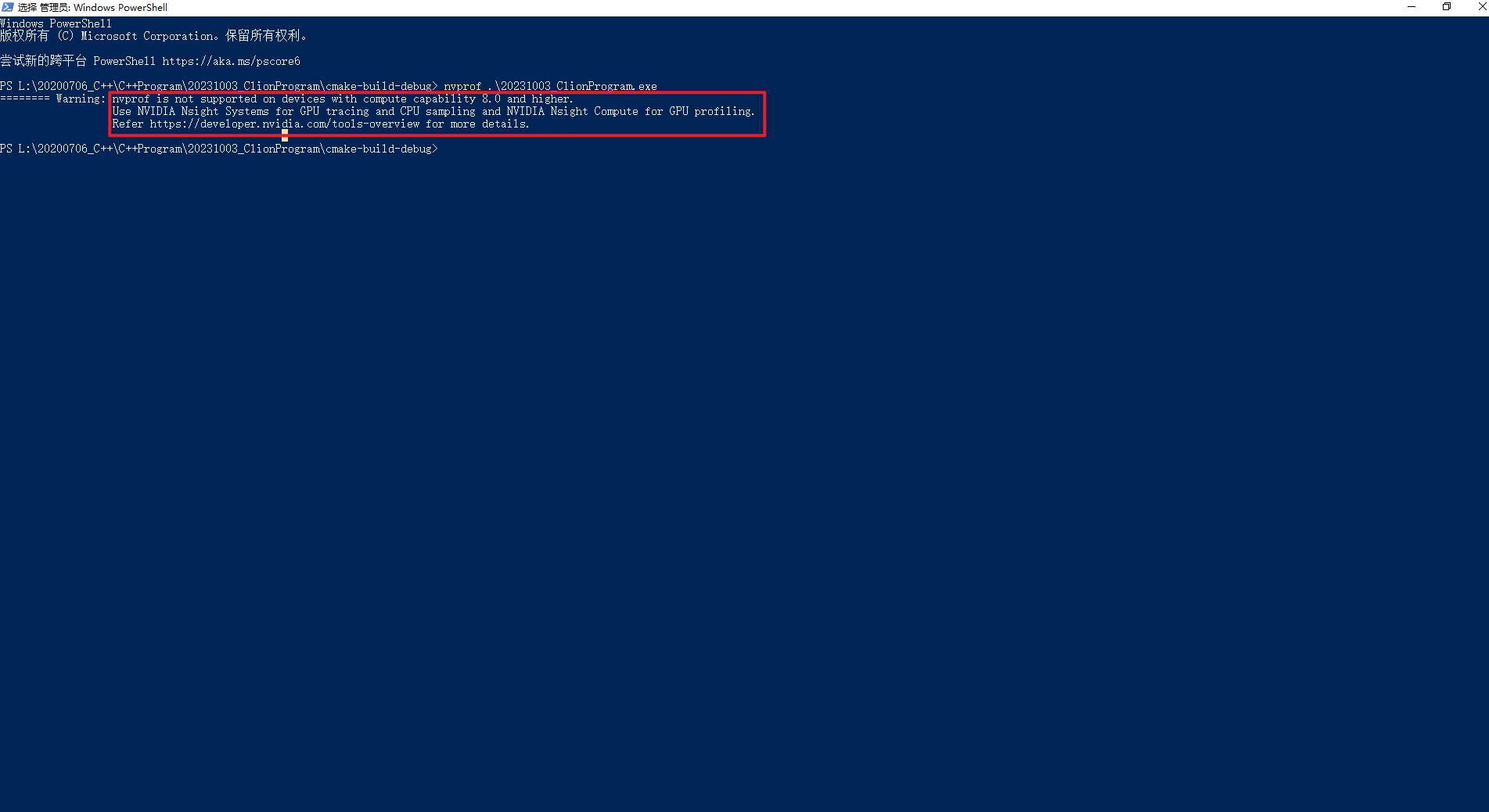
说明:对于计算能力为8.0及更高版本的设备,不支持使用nvprof。对于GPU跟踪和CPU采样,使用NVIDIA Nsight Systems;对于GPU分析,使用N服务器托管网VIDIA Nsight Compute。
这部分还不熟悉,先简要介绍,后续深入研究。Nsight是NVIDIA面相开发者提供的开发工具套件,能提供深入的跟踪、调试、评测和分析,以优化跨NVIDIA GPU和CPU的复杂计算应用程序。Nsight主要包含Nsight System、Nsight Compute、Nsight Graphics三部分。
(1)Nsight System
所有与NVIDIA GPU相关的程序开发都可以从Nsight System开始以确定最大的优化机会。Nsight System给开发者一个系统级别的应用程序性能的可视化分析。开发人员可以优化瓶颈,以便在任意数量或大小的CPU和GPU之间实现高效扩展[4]。
(2)Nsight Compute
Nsight Compute是一个CUDA应用程序的交互式kernel分析器。它通过用户接口和命令行工具的形式提供了详细的性能分析度量和API调试。Nsight Compute还提供了定制化的和数据驱动的用户接口和度量集合,可以使用分析脚本对这些界面和度量集合进行扩展,以获得后处理的结果[5]。
(3)Nsight Graphics
Nsight Graphics是一个用于调试、评测和分析Microsoft Windows和Linux上的图形应用程序。它允许您优化基于Direct3D 11,Direct3D 12,DirectX,Raytracing 1.1,OpenGL,Vulkan和KHR Vulkan Ray Tracing Extension的应程序的性能[6]。
3.CUDA数据类型
CUDA支持多种数据类型,包括标准的C/C++数据类型以及特定于CUDA的数据类型。常见的CUDA数据类型,如下所示:
(1)基本数据类型(与C/C++相似)
int
float
double
char
unsigned int
short
long
unsigned char
unsigned short
unsigned long
bool
void
signed int或signed
signed char
signed short
signed long
signed long long
unsigned long long
(2)向量数据类型
int1, int2, int3, int4: 1到4个整数元素的向量。
float1, float2, float3, float4: 1到4个浮点数元素的向量。
double1, double2, double3, double4: 1到4个双精度浮点数元素的向量。
(3)复数数据类型
cuComplex: 单精度复数。
cuDoubleComplex: 双精度复数。
(4)CUDA数据类型修饰符
__device__: 用于声明在设备上执行的函数或变量。
__constant__: 用于声明常量内存。
__shared__: 用于声明共享内存。
__global__: 用于声明全局内核函数。
(5)CUDA特定的数据类型
dim3: 三维坐标,通常用于线程和块的索引。
cudaStream_t: 用于管理CUDA流。
cudaEvent_t: 用于事件同步。
texture: 用于声明纹理内存,支持不同的数据类型和维度。
除此之外CUDA还支持通过typedef和struct等方式定义自定义数据类型,以满足特定应用程序的需求。
4.C++数据类型
C++中数据类型完整列表,包括基本数据类型、复合数据类型和一些特殊数据类型,如下所示:
(1)基本数据类型
int
float
double
char
bool
void
wchar_t(宽字符类型)
short(或short int)
long(或long int)
long long(或long long int)
unsigned int
unsigned char
unsigned short
unsigned long
unsigned long long
(2)复合数据类型
array(数组)
struct(结构体)
union(联合体)
enum(枚举)
class(类)
(3)其它数据类型
signed(通常与int、char、short和long配合使用,表示有符号类型)
auto(C++11引入的自动类型推导)
decltype(C++11引入的类型推导)
nullptr(C++11引入的空指针)
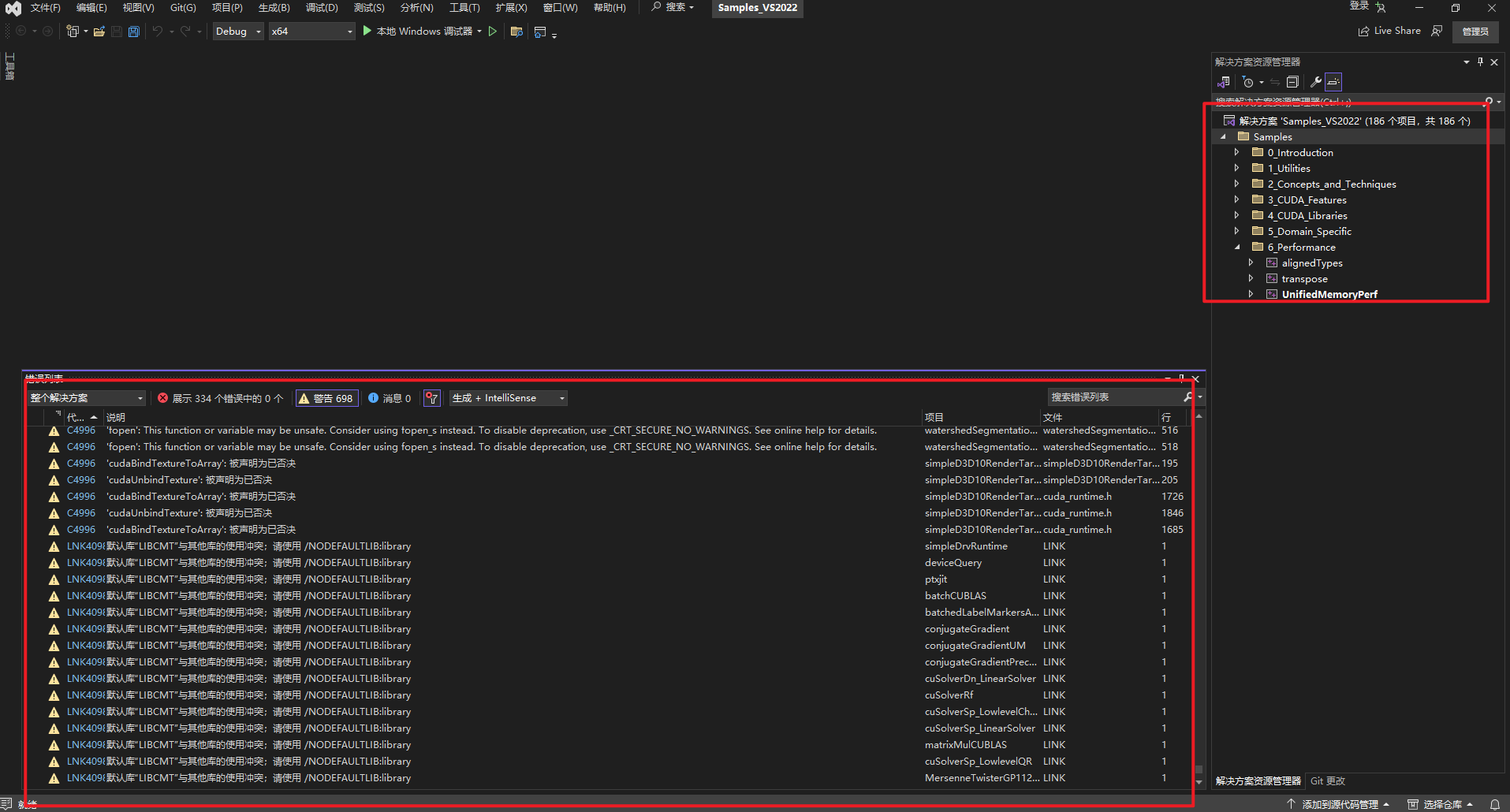
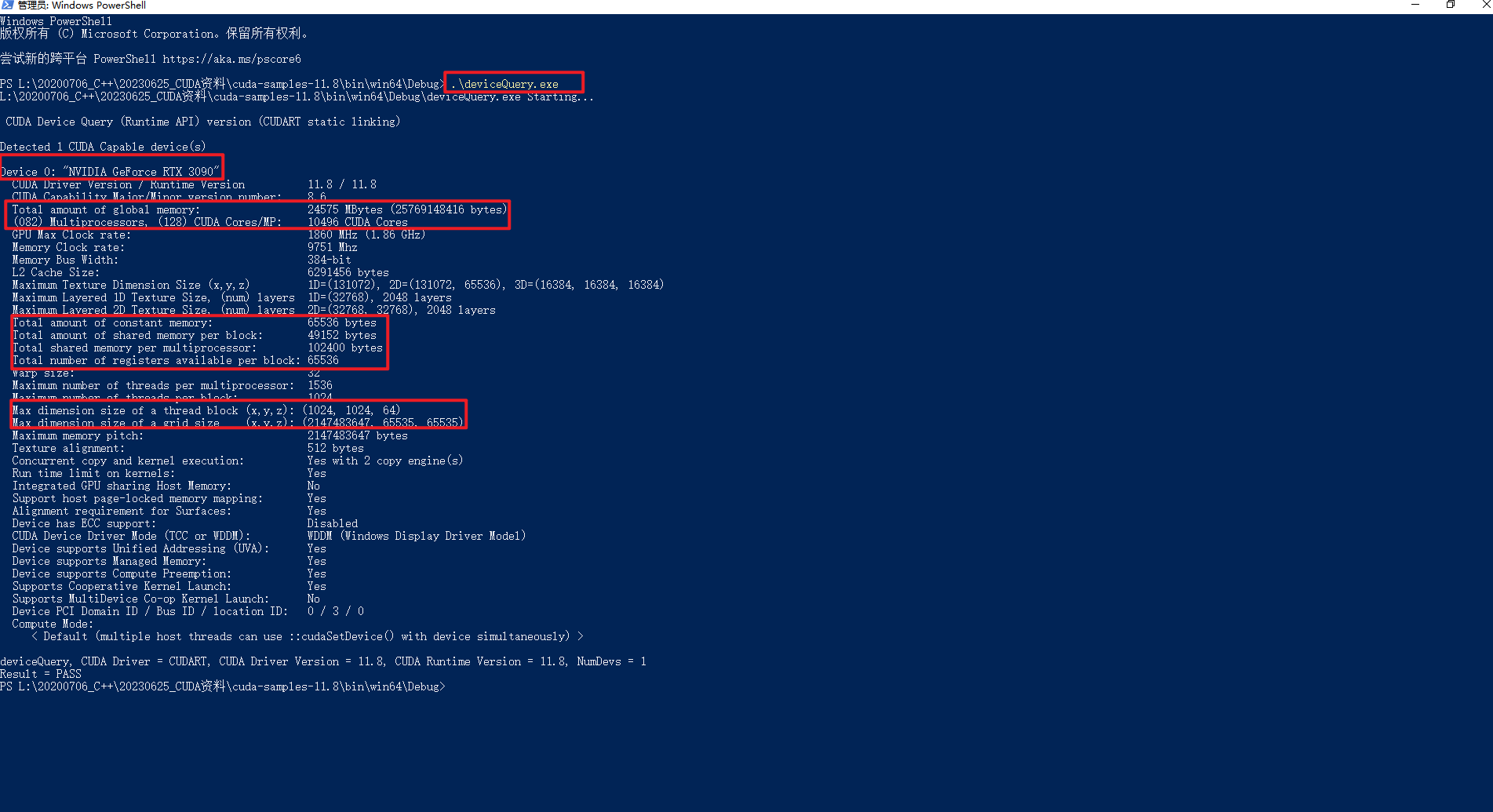
5.通过deviceQuery.exe查下设备信息
因为本地安装CUDA 11.8版本,所以下载https://github.com/NVIDIA/cuda-samples/releases/tag/v11.8,然后使用VS2022打开Samples_VS2022.sln编译,如下所示:
执行.deviceQuery.exe后可以看到很多熟面孔的常量信息,如下所示:
参考文献:
[1]NVIDIA Developer Tools:https://developer.nvidia.com/tools-overview
[2]《CUDA C编程权威指南》
[3]使用Nsight工具分析优化应用程序:https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/GPU/s/el8mizux4
[4]https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-systems
[5]https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-compute
[6]https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-graphics
[7]给核函数计时:https://github.com/ai408/nlp-engineering/tree/main/20230917_NLP工程化/20231004_高性能计算/20231003_CUDA编程/20231003_CUDA_C编程权威指南/2-CUDA编程模型/2.2-给核函数计时
服务器托管,北京服务器托管,服务器租用 http://www.fwqtg.net
机房租用,北京机房租用,IDC机房托管, http://www.fwqtg.net
简述 深度优先和广度优先是在图和树的遍历搜索中比较常用的搜索方法 内容 广度优先搜索和深度优先搜索一样,都是对图进行搜索的算法,都是从起点开始顺着边搜索,此时并不知道图的整体结构,直到找到指定节点(即终点)。在此过程中每走到一个节点,就会判断一次它是否为终点;…

