配置文件的webhook支持discord,所以尝试使用钉钉和企业微信。
WebHook {
Discord {
Url = ""
AvatarUrl = ""
User = "announcer"
}
}
服务端中判断如果配置了webhook会在自身添加agent之前就转发给discord了。
func (t *Teamserver) AgentAdd(Agent *agent.Agent) []*agent.Agent {
if Agent != nil {
if t.WebHooks != nil {
t.WebHooks.NewAgent(Agent.ToMap())
}
}
...
}
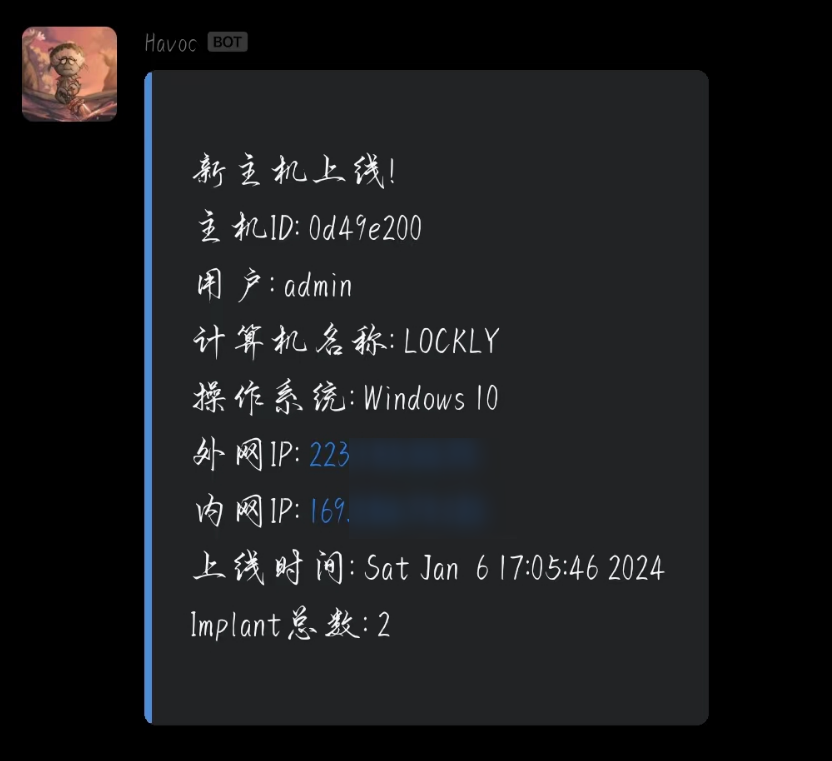
可以看到在上线时,server的控制台上会有上线的信息。
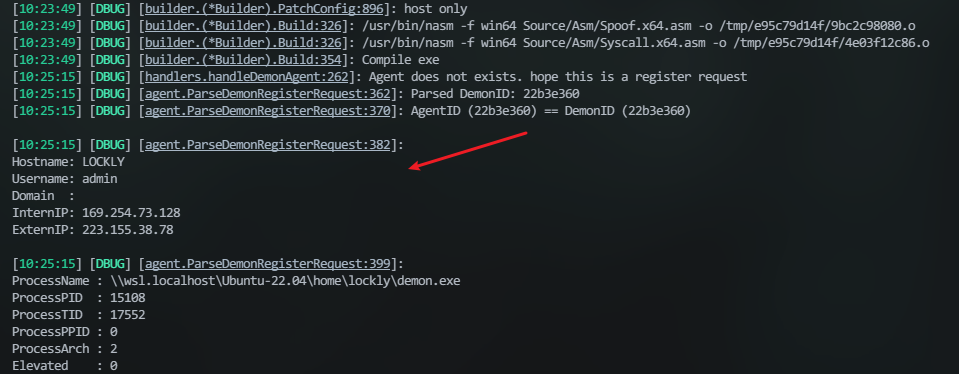
借鉴一个老哥的做法:起个子程序来开服务端,同时监听并捕获这个信息:
process = subprocess.Popen(['./havoc', 'server', '--profile', './profiles/havoc.yaotl', '-v', '--debug'],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
text=True)
capture = False
// 获取到前四行即可
if "[DBUG] [agent.ParseDemonRegisterRequest:382]" in line:
capture = True
captured_text = ""
line_count = 0
continue
if capture:
if line_count 然后根据官方文档 发送text类型的消息,markdown可以但是在微信中不能正常显示。
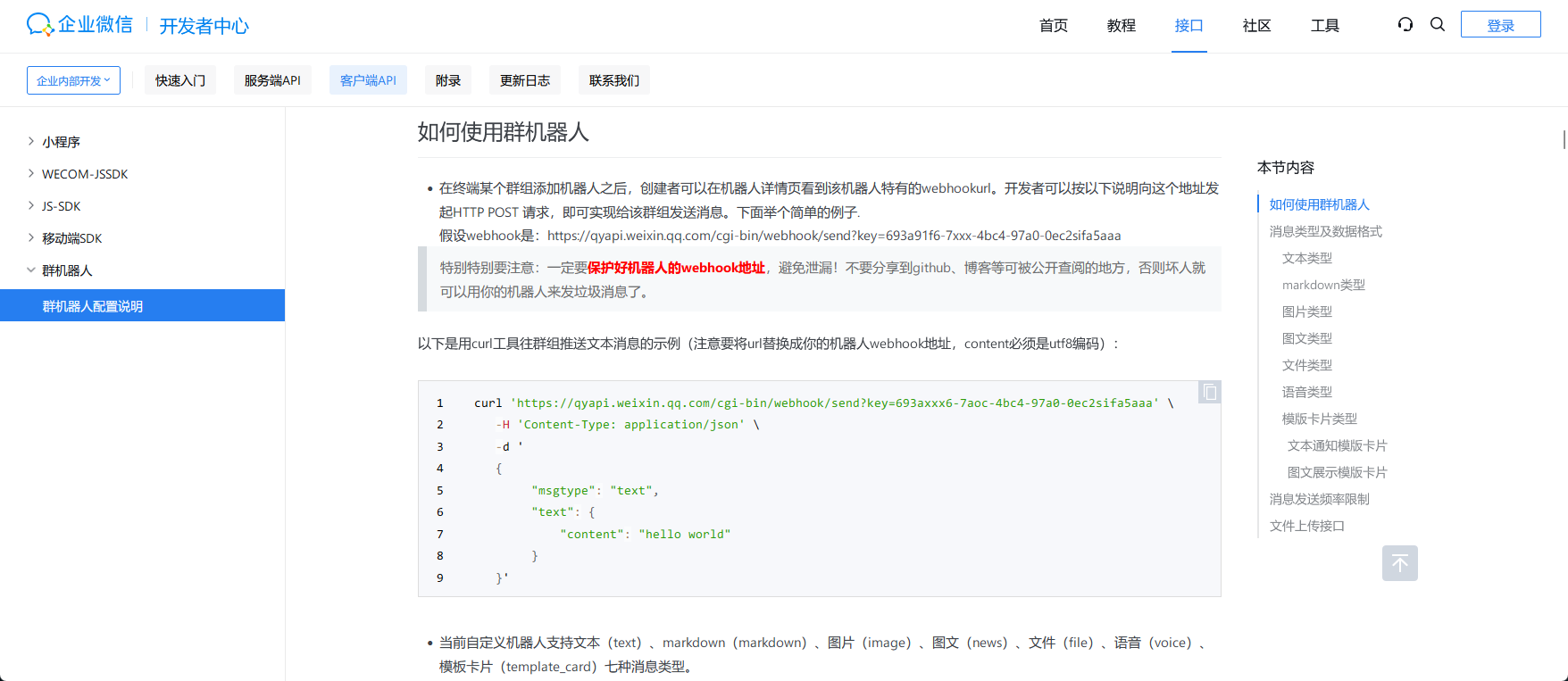
上面是markdown下面是text文本,代码也上传了:gayhub
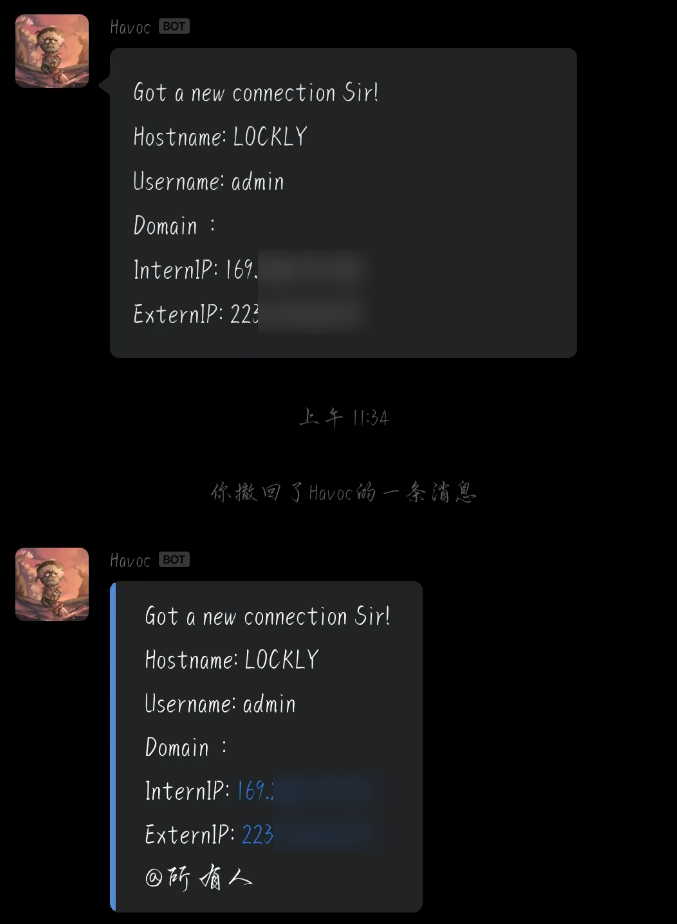
但这样并不是很好,而翻官方文档,里面有提供对客户端api的详细说明,主要涉及到havoc和havocui这两个。
对于ui可以直接在客户端的console中尝试他的效果:
像获取demons的数量可以用havoc.GetDemons()
文档中介绍了一些比较常用的api,在clientsrcHavocPythonApi有更多的调用方向,比如下面的:
PyMemberDef PyDemonClass_members[] = {
{ "Listener", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, Listener ), 0, "Listener name" },
{ "DemonID", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, DemonID ), 0, "Listener name" },
{ "ExternalIP", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, ExternalIP ), 0, "External IP" },
{ "InternalIP", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, InternalIP ), 0, "Internal IP" },
{ "User", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, User ), 0, "Username" },
{ "Computer", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, Computer ), 0, "Computer" },
{ "Domain", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, Domain ), 0, "Domain" },
{ "OS", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, OS ), 0, "Windows Version" },
{ "OSBuild", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, OSBuild ), 0, "Windows OS Build" },
{ "OSArch", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, OSArch ), 0, "Windows Architecture" },
{ "ProcessName", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, ProcessName ), 0, "Process Name" },
{ "ProcessID", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, ProcessID ), 0, "Process ID" },
{ "ProcessArch", T_STRING, offsetof( PyDemonClass, ProcessArch服务器托管网 ), 0, "Process Architecture" },
{ "CONSOLE_INFO", T_INT, offsetof( PyDemonClass, CONSOLE_INFO ), 0, "Console message type info" },
{ "CONSOLE_ERROR", T_INT, offsetof( PyDemonClass, CONSOLE_ERROR ), 0, "Console message type error" },
{ "CONSOLE_TASK", T_INT, offsetof( PyDemonClass, CONSOLE_TASK ), 0, "Console message type task" },
{ NULL },
};
PyMethodDef PyDemonClass_methods[] = {
{ "ConsoleWrite", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_ConsoleWrite, METH_VARARGS, "Prints messages to the demon sessions console" },
{ "ProcessCreate", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_ProcessCreate, METH_VARARGS, "Creates a Process" },
{ "InlineExecute", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_InlineExecute, METH_VARARGS, "Executes a coff file in the context of the demon sessions" },
{ "InlineExecuteGetOutput", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_InlineExecuteGetOutput, METH_VARARGS, "Executes a coff file in the context of the demon sessions and get the output via a callback" },
{ "DllSpawn", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_DllSpawn, METH_VARARGS, "Spawn and injects a reflective dll and get output from it" },
{ "DllInject", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_DllInject, METH_VARARGS, "Injects a reflective dll into a specified process" },
{ "DotnetInlineExecute", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_DotnetInlineExecute, METH_VARARGS, "Executes a dotnet assembly in the context of the demon sessions" },
{ "Command", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_Command, METH_VARARGS, "Run a command" },
{ "CommandGetOutput", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_CommandGetOutput, METH_VARARGS, "Run a command and retreive the output" },
{ "ShellcodeSpawn", ( PyCFunction ) DemonClass_ShellcodeSpawn, METH_VARARGS, "Executes shellcode spawning a new process" },
{ NULL },
};
代码的逻辑也很简单,就是通过havoc.Demon(demon_i服务器托管网d)获取到这个对象,抽出这里面的对象发送即可。代码可以去仓库看看。最终完成的效果如下:
最后也是正常能提示了,传送门:gayhub(一起交流)
服务器托管,北京服务器托管,服务器租用 http://www.fwqtg.net
机房租用,北京机房租用,IDC机房托管, http://www.fwqtg.net
数组 前言 1. 数组的概念 2. 一维数组的创建和初始化 2.1 数组创建 2.2 数组的初始化 2.3 数组的类型 3. 一维数组的使用 3.1 数组下标 3.2 数组元素的打印 3.3 数组的输入 4. 一维数组在内存中的存储 5. sizeof计算数组…

