文章目录
- 前言
- 缓存的实现
-
- Cache接口
- PerpetualCache
- 缓存的应用
-
- 缓存对应的初始化
- 一级缓存
- 二级缓存
- 第三方缓存
前言
MyBatis作为一个强大的持久层框架,缓存是其必不可少的功能之一,Mybatis中的缓存分为一级缓存和二级缓存。但本质上是一样的,都是使用Cache接口实现的。
缓存的实现
Cache接口
Cache接口是缓存模块中最核心的接口,它定义了所有缓存的基本行为。其实现类很多,但是大部分都是装饰器,只有PerpetualCache提供了Cache接口的基本实现。
PerpetualCache
PerpetualCache在缓存模块中扮演了ConcreteComponent的角色,其实现比较简单,底层使用HashMap记录缓存项,具体的实现如下:
/**
* 在装饰器模式用 用来被装饰的对象
* 缓存中的 基本缓存处理的实现
* 其实就是一个 HashMap 的基本操作
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id; // Cache 对象的唯一标识
// 用于记录缓存的Map对象
private final MapObject, Object> cache = new HashMap>();
public PerpetualCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return cache.size();
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Cache)) {
return false;
}
Cache otherCache = (Cache) o;
// 只关心ID
return getId().equals(otherCache.getId());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
// 只关心ID
return getId().hashCode();
}
}
cache.decorators包下提供的装饰器,他们都实现了Cache接口。这些装饰器都在PerpetualCache的基础上提供了一些额外的功能,通过多个组合实现一些特殊的需求。
其他的具体实现类,可以自行查阅。
| 缓存实现类 | 描述 | 作用 | 装饰条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基本缓存 | 缓存基本实现类 | 默认是PerpetualCache,也可以自定义比如RedisCache、EhCache等,具备基本功能的缓存类 | 无 |
| LruCache | LRU策略的缓存 | 当缓存到达上限时候,删除最近最少使用的缓存(Least Recently Use) | eviction=“LRU”(默认) |
| FifoCache | FIFO策略的缓存 | 当缓存到达上限时候,删除最先入队的缓存 | eviction=“FIFO” |
| SoftCacheWeakCache | 带清理策略的缓存 | 通过JVM的软引用和弱引用来实现缓存,当JVM内存不足时,会自动清理掉这些缓存,基于SoftReference和WeakReference | eviction=”SOFT”eviction=“WEAK” |
| LoggingCache | 带日志功能的缓存 | 比如:输出缓存命中率 | 基本 |
| SynchronizedCache | 同步缓存 | 基于synchronized关键字实现,解决并发问题 | 基本 |
| BlockingCache | 阻塞缓存 | 通过在get/put方式中加锁,保证只有一个线程操作缓存,基于Java重入锁实现 | blocking=true |
| SerializedCache | 支持序列化的缓存 | 将对象序列化以后存到缓存中,取出时反序列化 | readOnly=false(默认) |
| ScheduledCache | 定时调度的缓存 | 在进行get/put/remove/getSize等操作前,判断缓存时间是否超过了设置的最长缓存时间(默认是一小时),如果是则清空缓存–即每隔一段时间清空一次缓存 | flushInterval不为空 |
| TransactionalCache | 事务缓存 | 在二级缓存中使用,可一次存入多个缓存,移除多个缓存 | 在TransactionalCacheManager中用Map维护对应关系 |
缓存的应用
缓存对应的初始化
在Configuration初始化的时候会为各种Cache实现注册对应的别名
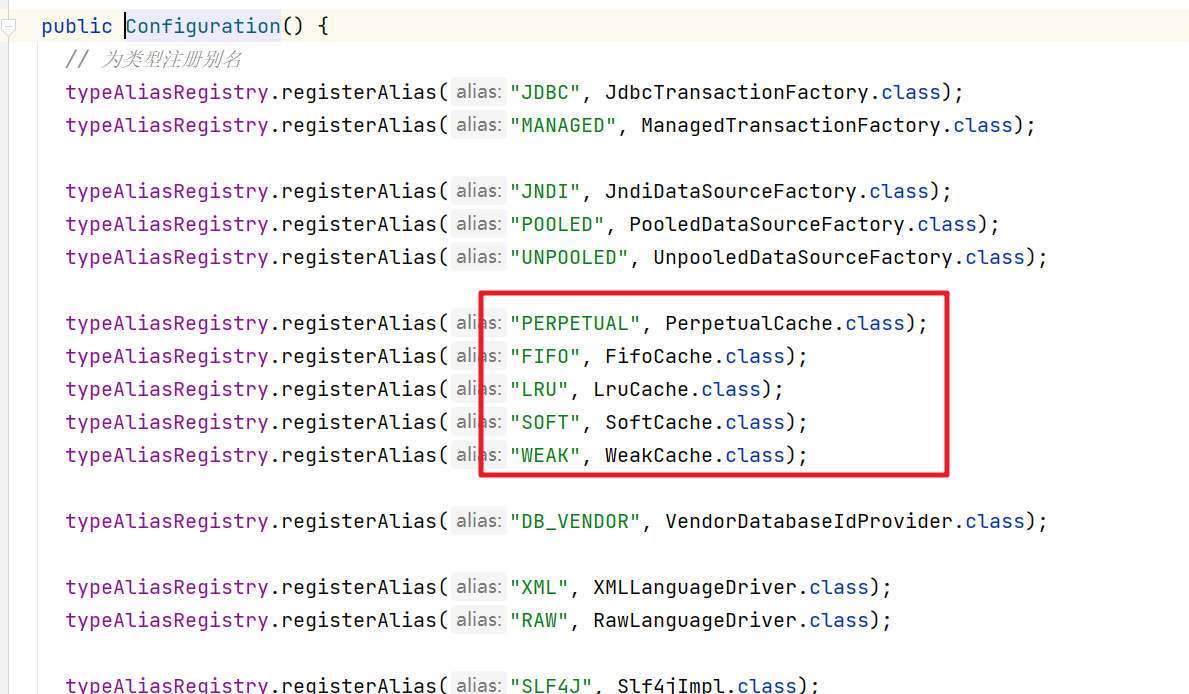
在解析settings标签的时候,设置的默认值有如下
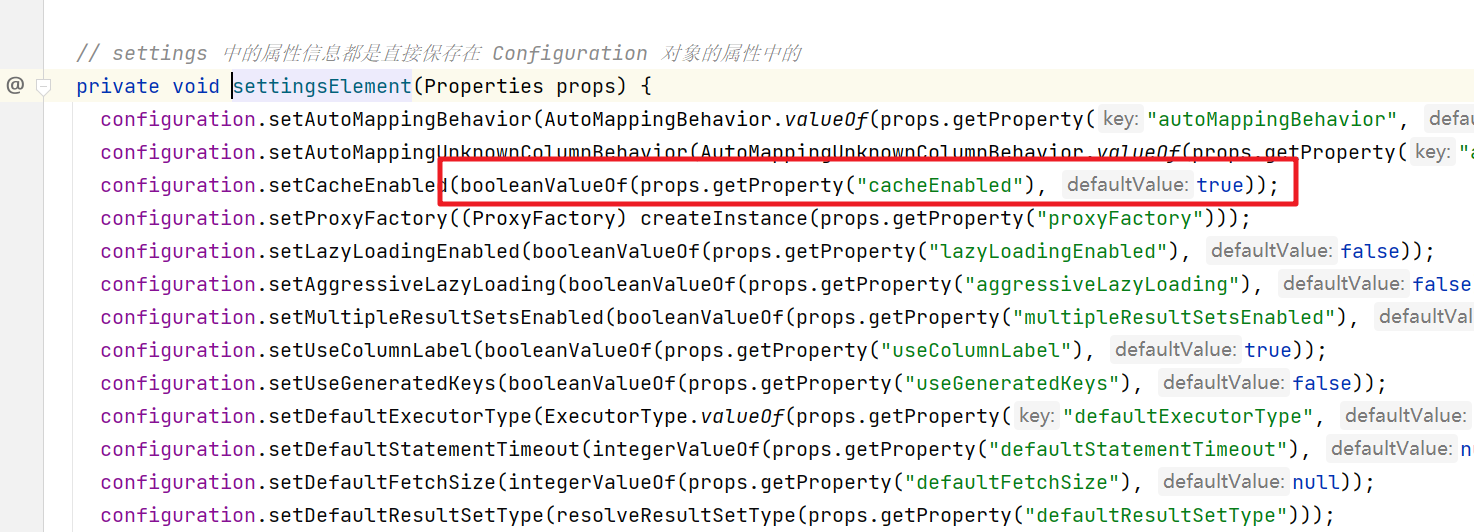
cacheEnabled默认为true,localCacheScope默认为 SESSION
在解析映射文件的时候会解析相关的cache标签
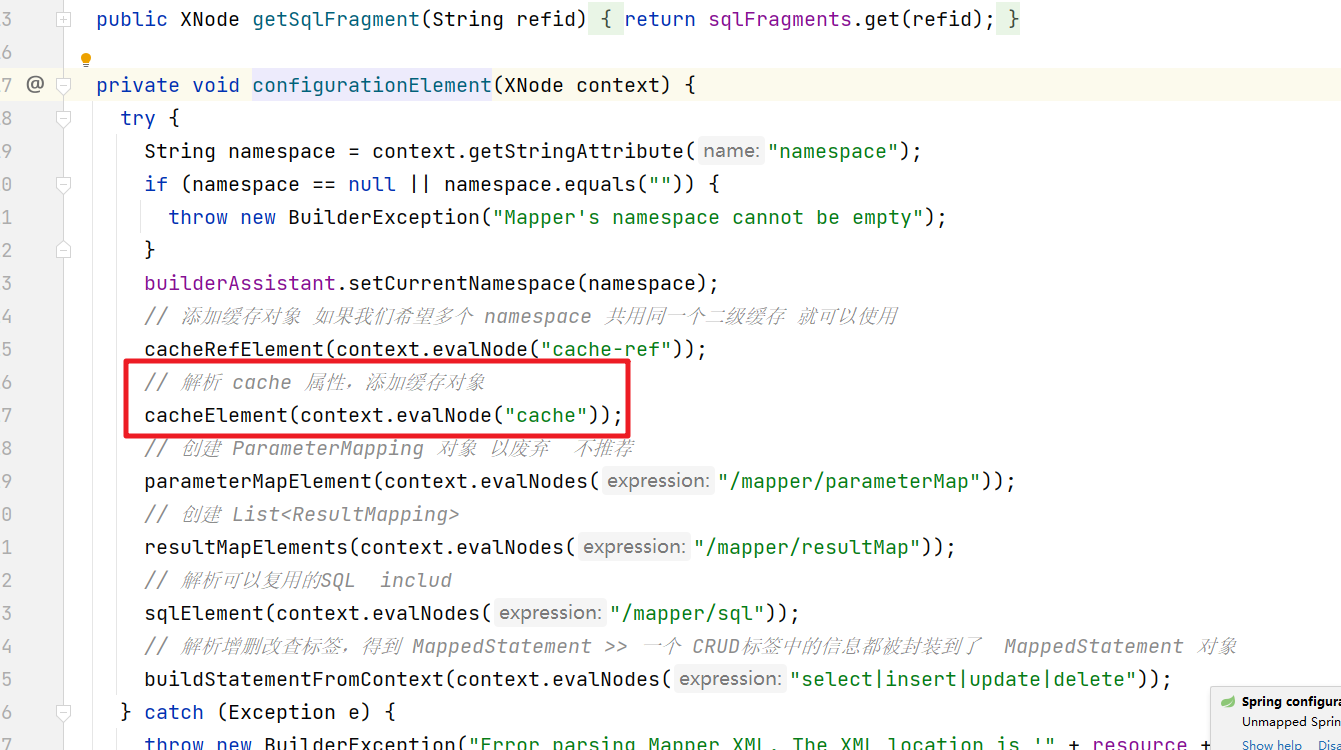
然后解析映射文件的cache标签后会在Configuration对象中添加对应的数据
private void cacheElement(XNode context) {
// 只有 cache 标签不为空才解析
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}
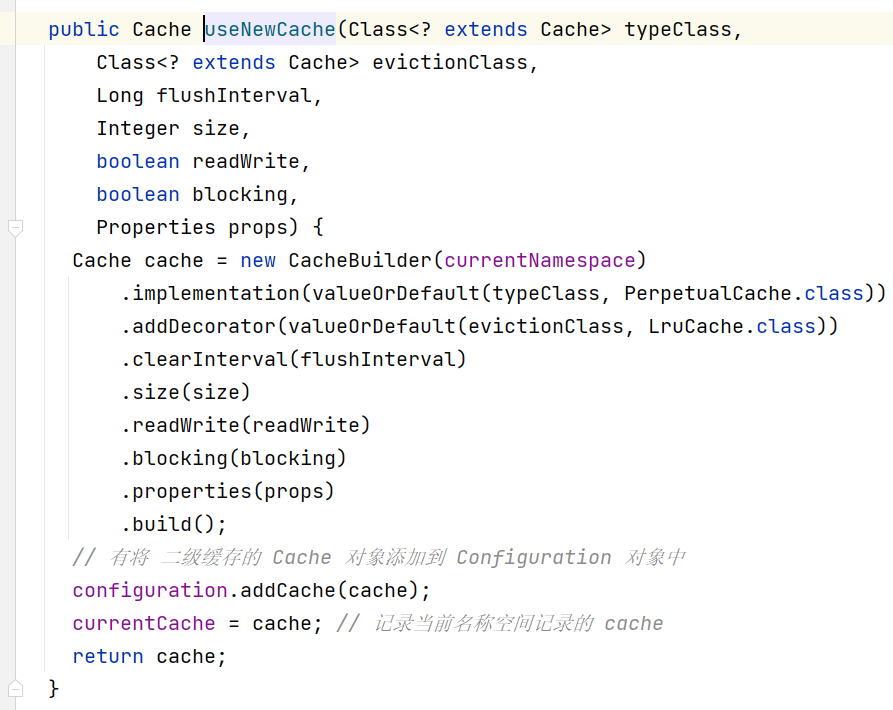
如果存储 cache 标签,那么对应的 Cache对象会被保存在 currentCache 属性中,保存在了 MapperStatement 对象的 cache 属性中。
在openSession的时创建对应的执行器的时候会有缓存的操作
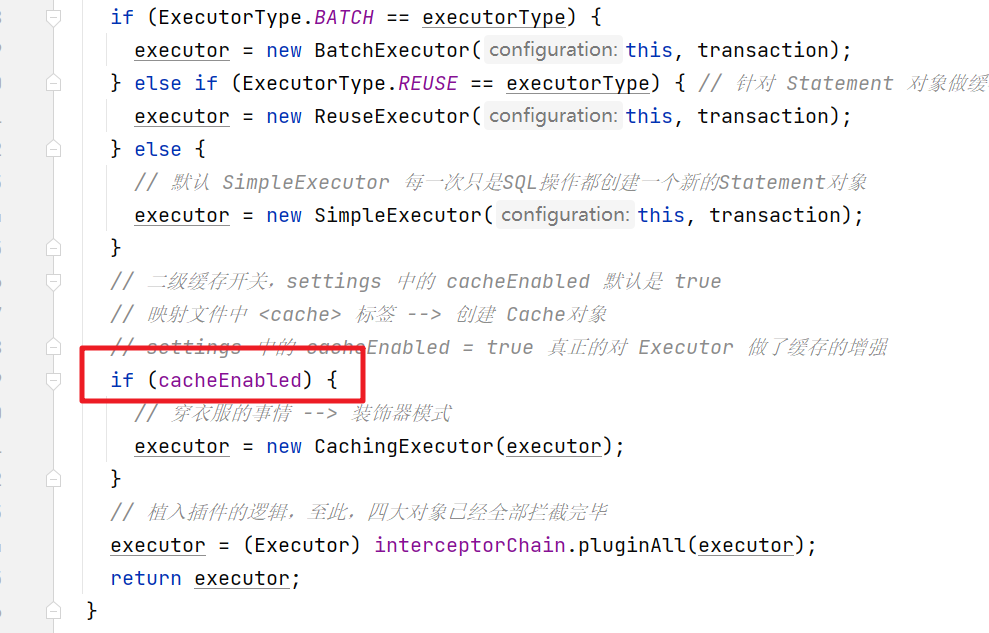
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
// 默认 SimpleExecutor
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 二级缓存开关,settings 中的 cacheEnabled 默认是 true
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 植入插件的逻辑,至此,四大对象已经全部拦截完毕
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
如果 cacheEnabled 为 true 就会通过 CachingExecutor 来装饰executor 对象,在执行SQL操作的时候会涉及到缓存的具体使用。这个就分为一级缓存和二级缓存.
一级缓存
一级缓存也叫本地缓存(Local Cache),MyBatis的一级缓存是在会话(SqlSession)层面进行缓存的。MyBatis的一级缓存是默认开启的,不需要任何的配置(如果要关闭,localCacheScope设置为STATEMENT)。在BaseExecutor对象的query方法中有关闭一级缓存的逻辑
因为一级缓存是Session级别的缓存,肯定需要在Session范围内创建,其实PerpetualCache的实例化是在BaseExecutor的构造方法中创建的
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.transaction = transaction;
this.deferredLoads = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue>();
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
this.localOutputParameterCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalOutputParameterCache");
this.closed = false;
this.configuration = configuration;
this.wrapper = this;
}
一级缓存的具体实现也是在BaseExecutor的query方法中来实现的
public E> ListE> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 异常体系之 ErrorContext
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
// flushCache="true"时,即使是查询,也清空一级缓存
clearLocalCache();
}
ListE> list;
try {
// 防止递归查询重复处理缓存
queryStack++;
// 查询一级缓存
// ResultHandler 和 ResultSetHandler的区别
list = resultHandler == null ? (ListE>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 真正的查询流程
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
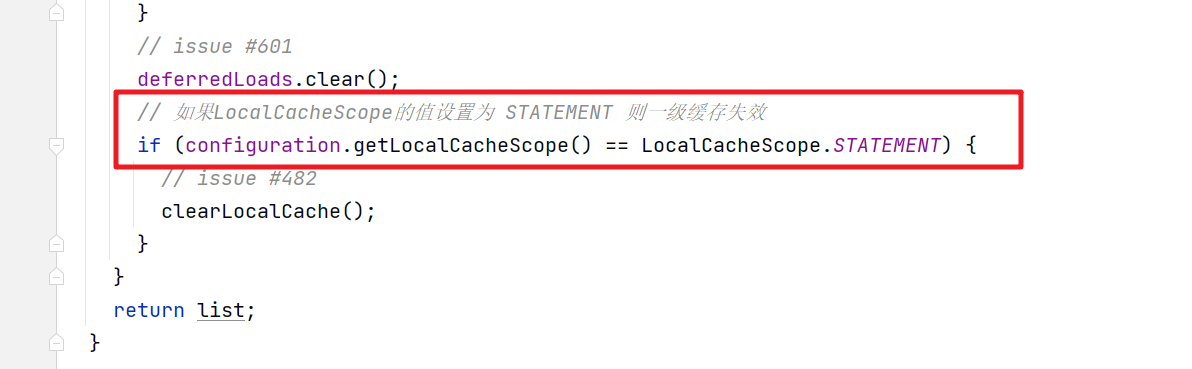
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
一级缓存的验证:
同一个Session中的多个相同操作
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
// 1.获取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 2.加载解析配置文件并获取SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory factory = new 服务器托管网SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
// 3.根据SqlSessionFactory对象获取Sql服务器托管网Session对象
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
// 4.通过SqlSession中提供的 API方法来操作数据库
ListUser> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserList");
System.out.println(list.size());
// 一级缓存测试
System.out.println("---------");
list = sqlSession.selectList("com.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserList");
System.out.println(list.size());
// 5.关闭会话
sqlSession.close();
}
通过日志的输出结果会看到第二次selectList没有进行sql查询。不同的Session中的相同操作,一级缓存是没有起作用的。
二级缓存
二级缓存是用来解决一级缓存不能跨会话共享的问题的,范围是namespace级别的,可以被多个SqlSession共享。
二级缓存的设置,首先是settings中的cacheEnabled要设置为true,默认的就是为true,这个步骤决定了在创建Executor对象的时候是否通过CachingExecutor来装饰。
设置了cacheEnabled标签为true后还需要在对应的映射文件中添加 cache 标签才行。
cache type="org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpetualCache"
size="1024" >
eviction="LRU" !—回收策略-->
flushInterval="120000" !—自动刷新时间 ms,未配置时只有调用时刷新-->
readOnly="false"/> !—默认是false(安全),改为true可读写时,对象必须支持序列化 -->
cache属性详解:
| 属性 | 含义 | 取值 |
|---|---|---|
| type | 缓存实现类 | 需要实现Cache接口,默认是PerpetualCache,可以使用第三方缓存 |
| size | 最多缓存对象个数 | 默认1024 |
| eviction | 回收策略(缓存淘汰算法) | LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象(默认)。FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。 |
| flushInterval | 定时自动清空缓存间隔 | 自动刷新时间,单位 ms,未配置时只有调用时刷新 |
| readOnly | 是否只读 | true:只读缓存;会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些对象不能被修改。这提供了很重要的性能优势。false:读写缓存;会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化),不会共享。这会慢一些,但是安全,因此默认是 false。改为false可读写时,对象必须支持序列化。 |
| blocking | 启用阻塞缓存 | 通过在get/put方式中加锁,保证只有一个线程操作缓存,基于Java重入锁实现 |
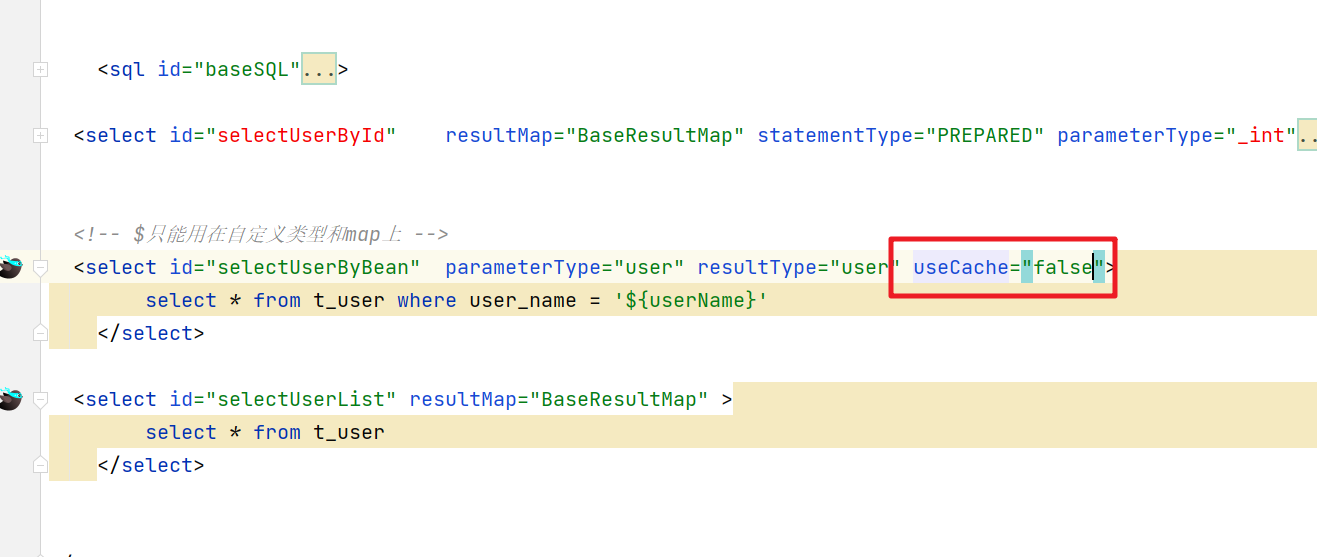
这样的设置表示当前的映射文件中的相关查询操作都会触发二级缓存,但如果某些个别方法我们不希望走二级缓存可以在标签中添加一个 useCache=false 来实现的设置不使用二级缓存。
当执行的对应的DML操作,在MyBatis中会清空对应的二级缓存和一级缓存。
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 增删改查的标签上有属性:flushCache="true" (select语句默认是false)
// 一级二级缓存都会被清理
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
第三方缓存
在实际开发的时候我们一般也很少使用MyBatis自带的二级缓存,这时我们会使用第三方的缓存工具Ehcache或者Redis来实现。
实现步骤:
添加依赖
dependency>
groupId>org.mybatis.cachesgroupId>
artifactId>mybatis-redisartifactId>
version>1.0.0-beta2version>
dependency>
添加redis的属性文件
host=192.168.0.10
port=6379
connectionTimeout=5000
soTimeout=5000
database=0
加上Cache标签的配置
cache type="org.mybatis.caches.redis.RedisCache"
eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size="512"
readOnly="true"/>
服务器托管,北京服务器托管,服务器租用 http://www.fwqtg.net
一、动态规划求解问题的思路 在《算法导论》上,动态规划的求解过程主要分为如下的四步: 描述最优解的结构 递归定义最优解的值 按自底向上的方式计算最优解的值 由计算出的结果构造一个最优解 在利用动态规划求解的过程中值得注意的就是是否包含最优子结构…

