Architecture and evolution of the modern web browser
这是一片很好的文章,太长,不想全文翻译,仅抽取部分,后来成了笔记,直接摘录。这篇文章写于2006年,与现在有两年多的时间,这期间由于给予手持设备的浏览器得到了很大的发展,但是主流产品仍然还是文章中所列举的那些。
浏览器的历史:
这段推荐看看:现在比较流向的浏览器有IE、firefox、safari、opera,除了没有提到后生的chrome,基本上都涉及。
Although key concepts can be traced back to systems envisioned by Vannevar Bush in the 1940s and Ted Nelson in the 1960s, the WWW was first described in a proposal written by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990 at the European Nuclear Research Center (CERN) (Berners-Lee, 1999). By 1991, he had written the first web browser, which was graphical and also served as an HTML editor. Around the same time, researchers at the University of Kansas had independently begun work on a text-only hypertext browser called Lynx; they adapted it to support the web in 1993. In the same year, the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) released a graphical web browser called Mosaic, which allowed users to view images directly interspersed with text. As the commercial potential of the web began to grow, NCSA founded an offshoot company called Spyglass to commercialize its technologies and Mosaic’s primary developer, Marc Andreesen, left to co-found his own company, Netscape. In 1994, Berners-Lee founded the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) to guide the evolution of the web and promote interoperability among web technologies. In 1995, Microsoft released Internet Explorer (IE), based on code licensed from Spyglass, igniting a period of intense competition with Netscape known as the “browser wars.” Microsoft eventually came to dominate the market, and Netscape released its browser as open source under the name Mozilla in 1998. Figure 1 shows a timeline of the various releases of several prominent web browsers.
Since 1998, several Mozilla variations have appeared, reusing the browser core but offering alternative design decisions for user-level features. Firefox is a standalone browser with a streamlined user interface, eliminating Mozilla’s integrated mail, news, and chat clients. Galeon is a browser for the GNOME desktop environment that integrates with other GNOME applications and technologies. The open source Konqueror browser has also been reused: Apple has integrated its core subsystems into its OS X web browser, Safari, and Apple’s modifications have in turn been reused by other browsers. Internet Explorer’s closed source engine has also seen reuse: Maxthon, Avant, and NetCaptor each provide additional features to IE such as tabbed browsing and ad-blocking. Although each browser engine typically produces a similar result, there can be differences as to how web pages look and behave; Netscape 8, based on Firefox, allows the user to switch between IE-based rendering and Mozilla-based rendering on the fly.
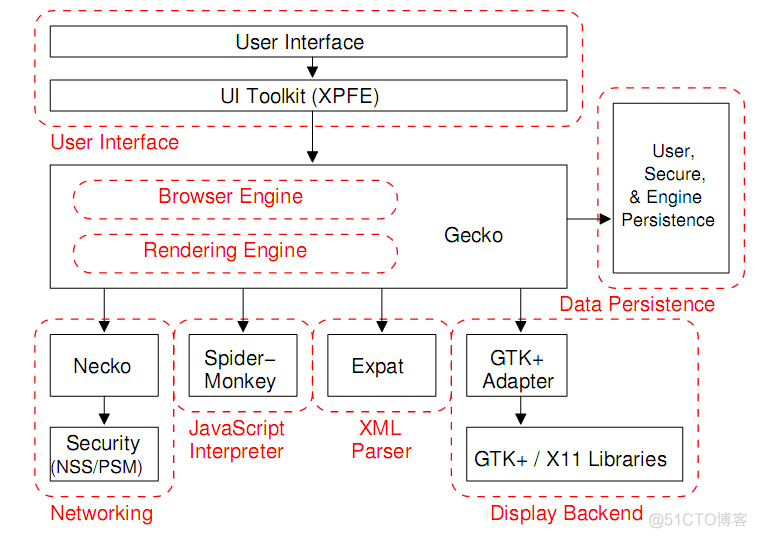
浏览器架构:
浏览器包括解析HTTP、JS,有些内容浏览器本身无法显示,例如Abobe flash,java applet,这些需要plugin来解决。除此之外,browser还提供一些辅助性的功能,例如书签,以往输入的记忆等等。
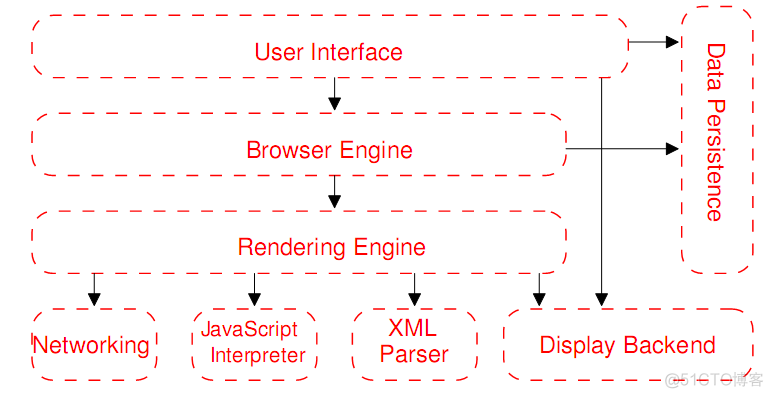
UI包括:Provides features such as toolbars, visual page-load progress, smart download handling, preferences, and printing. It may be integrated with the desktop environment to provide browser session management or communication with other desktop applications.
Browser Engine: provides a high-level interface to the Rendering Engine. It loads a given URI and supports primitive browsing actions such as forward, back, and reload. It provides hooks for viewing various aspects of the browsing session such as current page load progress and JavaScript alerts. It also allows the querying and manipulation of Rendering Engine settings.
Rendering Engine(排版引擎): produces a visual representation for a given URI. It is capable of displaying HTML and Extensible Markup Language (XML) (Bray et al., 2004) documents, optionally styled with CSS, as well as embedded content such as images. It calculates the exact page layout and may use “reflow” algorithms to incrementally adjust the position of elements on the page. This subsystem also includes the HTML parser.
Networking:implements file transfer protocols such as HTTP and FTP. It translates between different character sets, and resolves MIME media types for files. It may implement a cache of recently retrieved resources.
JS Interpreter:evaluates JavaScript (also known as ECMA-Script) code, which may be embedded in web pages. JavaScript is an object-oriented scripting language developed by Netscape. Certain Java-Script functionality, such as the opening of pop-up windows, may be disabled by the Browser Engine or Rendering Engine for security purposes.
XML Parser : parses XML documents into a Document Object Model (DOM) tree. This is one of the most reusable subsystems in the architecture. In fact, almost all browser implementations leverage an existing XML Parser rather than creating their own from scratch.
Display Backend : provides drawing and windowing primitives, a set of user interface widgets, and a set of fonts. It may be tied closely with the operating system.
Data persistence : stores various data associated with the browsing session on disk. This may be high-level data such as bookmarks or toolbar settings, or it may be low-level data such as cookies, security certificates, or cache.
|
|
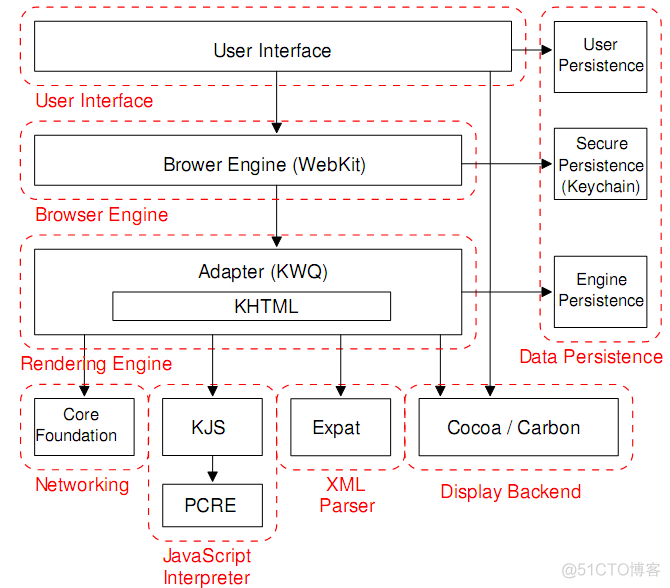
这是对比mozilla的web浏览器结构和框架。mozilla的Rendering引擎比较庞大,一方面它能很出色地对有误的或者中断的HTLM进行解析,另一个方面提供了应用跨平台的UI,由它的XUL语言提供。 firefox是mozilla的一个变种,它删除了mozilla集成的mail,news、chat,它一个特点就是非常强大的扩展能力。这些扩展可以挂在浏览器不同的level。我觉得讽刺的是集成所有这些是目前的一个趋势。这是山水轮流转。 |
|
|
Safari Apple为他的Mac OS X操作系统提供的web浏览器,第一个版本在2003年1月释放,因为iPhone的流行而广被国人认知。它使用了KDE项目中的KHTML,KJS,修改后的版本称为WebCore和JavaScriptCore,license为LPGL,剩余的code是私有的。 在2005年safari释放了另一个版本,使用了webkit framwork,这是现在所熟悉的方式。 |
我觉得这篇文章能够很好地在框架上给出概况和指引,将便于我们学习webkit。
服务器托管,北京服务器托管,服务器租用 http://www.fwqtg.net
机房租用,北京机房租用,IDC机房托管, http://www.e1idc.net